Basic principles of Ethernet technology
Generally, what we mean by Ethernet mainly refers to the following three different LAN technologies:
Ethernet / IEEE 802.3: Coaxial cable is used as the network medium, and the transmission rate reaches 10Mbps;
100Mbps Ethernet: also known as Fast Ethernet, using twisted pair as network media, the transmission rate reaches 100Mbps;
1000Mbps Ethernet: also known as Gigabit Ethernet, using fiber optic cable or twisted pair as network media, the transmission rate reaches 1000Mbps (1Gbps)
With its highly flexible, relatively simple, and easy-to-implement features, Ethernet has become the most important LAN construction technology today. Although other network technologies were once considered to be able to replace the status of Ethernet, the vast majority of network managers still regard Ethernet as the preferred network solution.
In order to make Ethernet more complete and solve the various problems and limitations faced, some industry leading manufacturers and standard-setting organizations continue to revise and improve the Ethernet specifications. Perhaps, some people think that the expansion performance of Ethernet is relatively poor, but the transmission mechanism adopted by Ethernet is still an important foundation for current network data transmission.
How Ethernet works
Ethernet is a baseband local area network technology developed by Xeros, using coaxial cable as the network media, using carrier multiple access and collision detection (CSMA / CD) mechanism, and the data transmission rate reaches 10Mbps. Although Ethernet was first developed by Xeros in the 1970s, the term Ethernet is now more commonly used to refer to various LANs that use CSMA / CD technology.
Ethernet was designed to meet the needs of non-persistent network data transmission, and the IEEE 802.3 specification was formulated in 1980 based on the original Ethernet technology. Ethernet version 2.0 was jointly developed by Digital Equipment CorporaTIon, Intel, and Xeros, and is compatible with the IEEE 802.3 specification.
The schematic diagram of the Ethernet structure is as follows: 
Ethernet / IEEE 802.3 is usually implemented using a dedicated network interface card or through a circuit on the main circuit board of the system. Ethernet uses transceivers to connect to network media. The transceiver can perform multiple physical layer functions, including the detection of network collisions. The transceiver can be connected to the terminal station as an independent device via a cable, or it can be directly integrated into the network card of the terminal station.
Ethernet uses a broadcast mechanism, and all workstations connected to the network can see the data transmitted on the network. By looking at the target address contained in the frame, it is determined whether to receive or give up. If it proves that the data is indeed sent to itself, the workstation will receive the data and pass it to the higher-level protocol for processing.
Ethernet uses CSMA / CD media access mechanism, any workstation can access the network at any time. Before sending data, the workstation needs to listen to whether the network is idle. If there is no data transmission on the network, the workstation will put the information to be sent to the network. Otherwise, the workstation can only wait for the next time the network becomes idle before sending data.
As a network environment based on competition mechanism, Ethernet allows any network device to send information when the network is idle. Because there is no centralized management measures, it is very likely that multiple workstations simultaneously detect that the network is idle and send data to the network at the same time. At this time, the sent messages will collide with each other and cause damage. The workstation must wait for a period of time before resending the data. The compensation algorithm is used to determine when the workstation should retransmit the data frame after a collision.
Intelligent Street Lamps are also called intelligent lighting or smart street lights.It adopts the Internet of things and cloud computing technology to comprehensively upgrade the urban public lighting management system, so as to realize centralized control, operation and maintenance information and intelligent lighting of street lamps.The most advanced versions of Intelligent Street Lamps have been designed to create a happy atmosphere in roads, streets, squares and other places.The design of intelligent street lamps can only be designed by a wide range of discussions and environments that provide an aesthetic consistency.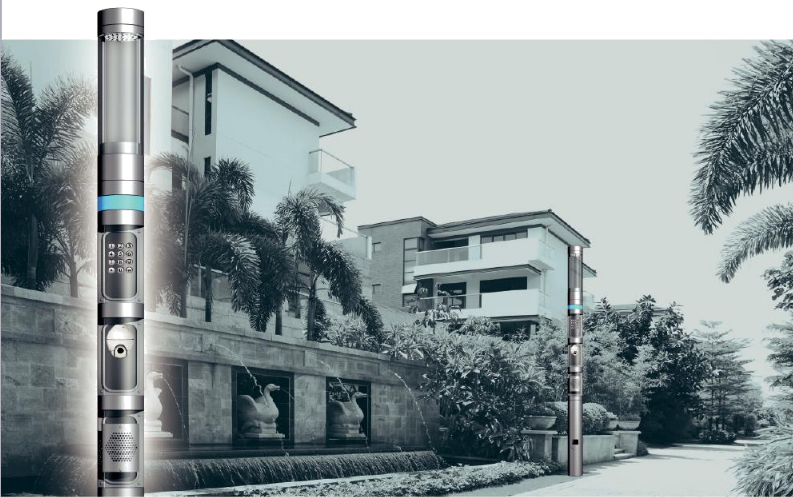
Intelligent Street Lamp system
The core functions of intelligent Street Lamp include Intelligent lighting,Smart city applications,The information publishing system,Intelligent security,Charging pile,Distributed monitoring sensor system.
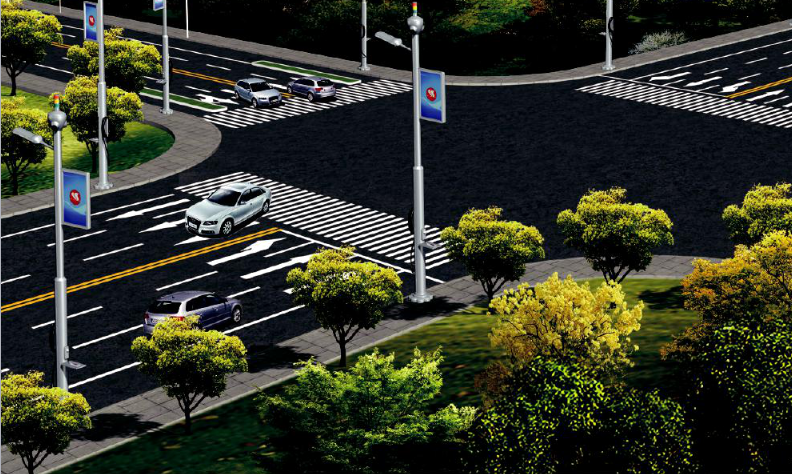

Product feature
1.Sensor
Sensor norise
Air pollution sensor
Temperature/humidity sensor
Brightness sensor
Municipal construction monitor
2.RFID
Special crowed monitor
CMC monitor
Community security monitor
Municipal facilities monitor
3.Communication Services
Micro base station
Street lights embedded WIFI hot spot
4.Video Monitor
Security monitor
Vehicle monitor
5.Emergency Broadcast
Active of the external field radio monitoring center
6.Intelligent Lighting
Cellular cooling technology
Based on the luminance uniformity of light distribution
Intelligent single lamp/center controller
Variety of modular design lamp,holder is optional.
7.Information Release
Advertising exposure
Current politics news
Information release
8.Charging Column
Electric car
Electric bicycle

Intelligent Street Lamp
Intelligent Street Lamp,Street Lamp,Street Lamp Post,Intelligent Lamp
Jiangsu chengxu Electric Group Co., Ltd , http://www.chengxulighting.com