What is a high-frequency wave? Many people have questions and don’t know how to answer this question.
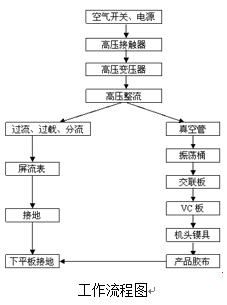
In fact, high-frequency waves are a type of ultrasonic waves, and their defining characteristic is frequency. When the frequency of an ultrasonic wave exceeds 100 kHz, it is classified as a high-frequency wave. These waves generate heat through friction, which is used for welding and bonding materials. For example, high-frequency plastic welders use this energy to join plastic components effectively.
A high-frequency plastic welding machine (commonly called a high-frequency machine or Hing frequency plastic welder) works by converting electrical energy into electromagnetic waves using an electronic tube. This creates a high-frequency electromagnetic field, which is then transmitted through various paths—such as the upper pole and the PVC tape between the cookware and ground—to induce movement in the polar molecules of the plastic. This motion generates heat, allowing the material to fuse under pressure.
The core technology of high-frequency machines lies in generating the high-frequency electromagnetic field. The vacuum tube in the welding machine converts high-voltage electricity into electromagnetic energy, which is then oscillated via the oscillating barrel to produce the field. The oscillation frequency directly affects the strength of the output, and thus the quality of the weld. Determining and adjusting this frequency is critical. However, in today’s automated environments, this process is still largely done manually by workers, which can lead to defects and increased costs. Using an electronic instrument to measure the optimal frequency is the most efficient solution.
Once the electromagnetic energy is amplified, the voltage can reach several thousand to tens of thousands of volts. Measuring the signal frequency in such a high-voltage environment requires careful consideration. An oscilloscope, a standard measuring tool, can handle this task. There are two common methods: direct measurement and induction. Direct measurement involves using a high-voltage attenuator probe to reduce the signal before inputting it into the oscilloscope. Induction, on the other hand, uses a passive probe to sense the electromagnetic field without direct contact with the circuit.
The induction method is safer and more cost-effective. It doesn't require touching the machine's internal components, making it less risky for both the equipment and the operator. Additionally, since it doesn't need expensive high-voltage probes, it's more economical. Therefore, it is the preferred method for measuring the oscillation frequency of high-frequency plastic welders.
Digital oscilloscopes offer two ways to measure frequency: software and hardware. The software method calculates the average period from stored waveforms and converts it into frequency. The hardware method uses a built-in frequency meter that counts trigger events per second. While both methods give similar results for regular waveforms, they differ significantly when dealing with irregular signals. In such cases, the hardware method provides more stable and accurate readings, especially when high precision is required—often up to three decimal places. Most standard oscilloscopes use passive crystals, but for higher accuracy, an active crystal is necessary. The Dingyang SDS1000CFL series offers a 6-bit real-time counting active crystal frequency meter, meeting strict measurement requirements.
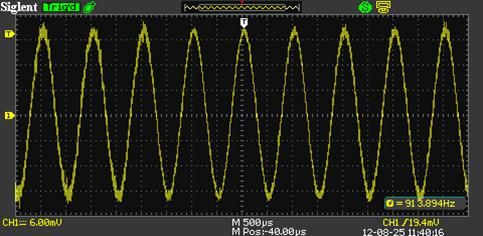
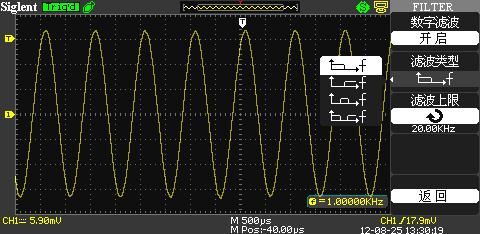
During actual measurements, I noticed significant noise interference, which affected the accuracy of the frequency readings. To address this, the oscilloscope needs strong noise filtering capabilities. The SDS1000CFL has advanced digital filtering options, including low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop filters. These help prevent false triggers caused by noise, ensuring more accurate measurements. For instance, when testing a 1KHz, 40mV signal, the oscilloscope displayed a measured value of 913.894Hz without filtering, but after enabling digital filtering, the reading stabilized at exactly 1KHz.
Inductive measurement differs from traditional methods. When using the inductive approach, a virtual probe is formed between the passive probe and the grounded alligator clip. As the electromagnetic field passes through the loop, it induces a current that is sent to the oscilloscope. Without grounding, the probe can act as a linear antenna, or it can be connected to the clip to form a loop antenna. Proper grounding is essential to avoid noise interference. Since only the frequency needs to be measured, the process is relatively simple: adjust the oscilloscope’s horizontal and vertical settings, enable digital filtering, and observe the frequency reading. This helps identify the optimal oscillation frequency for different products, improving production efficiency and yield.
This inductive method can also be applied to other high-frequency machines, showcasing the versatility of oscilloscopes in modern test and measurement applications. As technology advances, the role of oscilloscopes will continue to expand, becoming even more essential in industrial and scientific fields.
Hydraulic Pump Electric Motor Combo,A Hydraulic Pump,D B Hydraulics,Hydraulic dc motors
Wuxi Jinle Automobile Motor Factory , https://www.wxjldj.com