OpenWrt is a powerful open-source operating system designed for embedded systems, offering a flexible platform for learning and comparing different system architectures.
The following table provides a detailed comparison of the OpenWrt system architecture with other common system architectures:
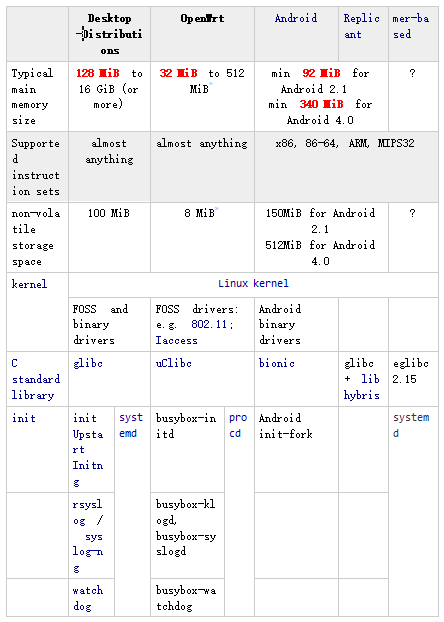
One of the main advantages of OpenWrt is its lightweight nature. It can run on as little as 32MB of RAM and requires only 8MB of flash storage. This makes it ideal for low-resource devices and allows it to support a wide range of hardware platforms, significantly reducing the cost of development and deployment. For smart products with limited functionality, OpenWrt offers a highly efficient and scalable solution.
In addition, OpenWrt uses the same Linux kernel as other major operating systems such as desktop distributions and Android. This compatibility allows developers to leverage existing tools and libraries, especially for wireless networking features like 802.11, giving OpenWrt more flexibility in wireless development.
Instead of using the standard GNU C Library (glibc), OpenWrt employs uClibc, a smaller and more lightweight C library specifically designed for embedded Linux systems. While glibc is built to support a broad range of hardware and software standards, uClibc sacrifices some features to save space, making it more suitable for resource-constrained environments.
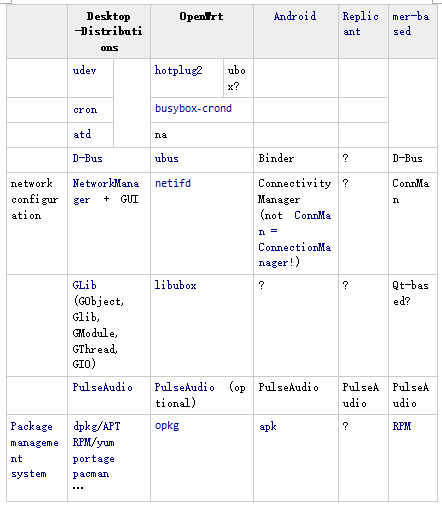
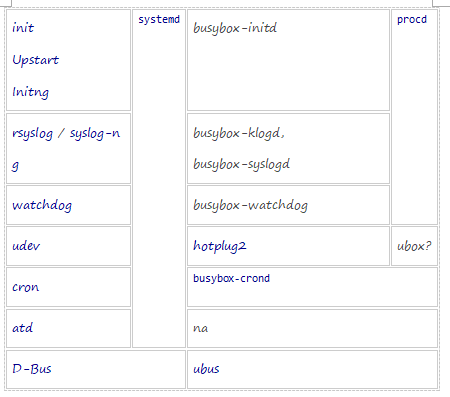
The file system initialization and management in OpenWrt differ from traditional Linux systems. The latest versions use a more centralized approach, with the procd daemon handling process control. Unlike the traditional init system, which starts from a single process, OpenWrt’s new startup mechanism integrates various components like hotplug2, ubox, and others. For example, the older version of OpenWrt used BusyBox for many utilities, while newer versions have replaced some of these with more modular tools. Crond still relies on BusyBox, but ubus provides a simplified API that is better suited for embedded systems.
Netifd is responsible for monitoring and configuring network interfaces, while libubox offers a set of utility functions for system management. Opkg is the package manager used in OpenWrt, similar to apt-get in Ubuntu or apk in Android, allowing users to easily install and manage software packages.
Overall, OpenWrt is an excellent choice for embedded systems due to its minimal resource requirements and high customizability. It runs efficiently on devices with at least 32MB of RAM and 8MB of flash memory. The latest version includes advanced tools like procd, ubox, ubus, netifd, and opkg, which streamline system management and improve performance. Whether you're building a small IoT device or a custom router, OpenWrt provides a robust and flexible foundation for your project.
Ejector Connector,Plug Row Connector,Ejector Header Socket,Ejector Header Connector
Dongguan ZhiChuangXing Electronics Co., LTD , https://www.zcxelectronics.com