A clock is the core component of a microcontroller, acting as the heartbeat that synchronizes all internal circuits. Imagine it like the beat in a radio broadcast during a morning exercise routine — "1234, 2234, 3234..." — where everyone moves in sync with the rhythm. The faster the beat, the quicker the actions; the slower the beat, the more relaxed the pace.
What's the difference between an internal and external clock?
Many PIC microcontrollers allow you to choose between an internal RC oscillator or an external clock source, such as a 4MHz quartz crystal. Some models even support multiple frequency options, giving developers flexibility in performance and power management.
For example, the PICLF1823 has an internal clock that can range from 31kHz up to 32MHz. This wide range opens up new possibilities for power optimization. While sleep mode is a common technique to reduce power consumption, the CPU remains idle during this time. However, if the CPU still needs to perform tasks while minimizing power usage, lowering the clock frequency becomes a highly effective strategy.
How do you set the clock?
Clock configuration typically involves two main areas: the configuration word and the oscillator control register (OSCCON). Let's take the PICLF1823 as an example.
The configuration word includes bits like FOSC<2:0> for selecting the oscillator type and PLLEN to enable the PLL. The OSCCON register is used to set the internal clock frequency and is usually not needed when using an external clock. Below is a detailed explanation of the OSCCON register from the data sheet.
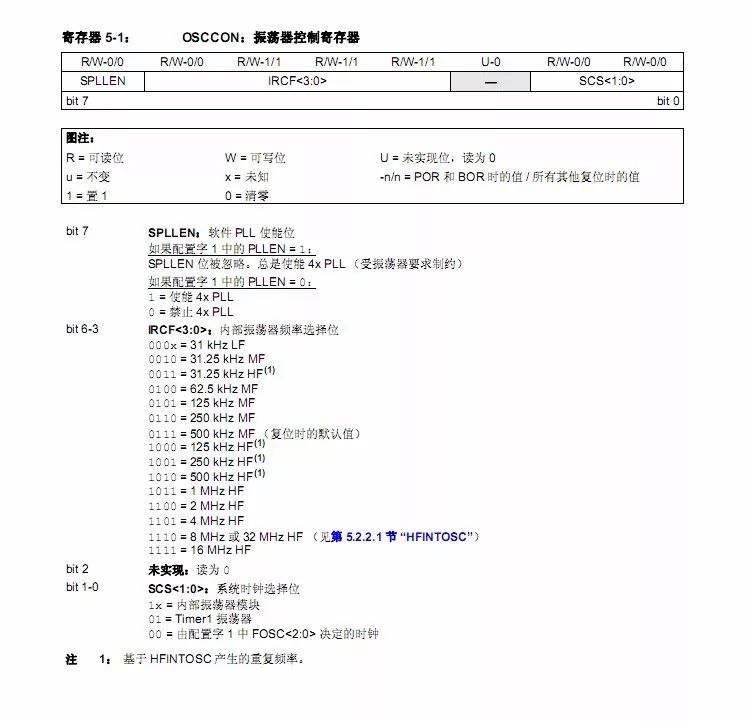
Example explanation:
Setting the clock to 8MHz using the internal oscillator.
Development environment: MPLAB X IDE
Chip model: PICLF1823
#include <xc.h>
__CONFIG(FOSC_INTOSC&WDTE_OFF&PWRTE_ON&MCLRE_OFF&CP_ON&CPD_OFF&BOREN_ON&
CLKOUTEN_OFF&IESO_ON&FCMEN_ON);
__CONFIG(PLLEN_OFF&LVP_OFF); // Set FOSC<2:0> to INTOSC
void init_fosc(void)
{
OSCCON = 0x70; // Select 8MHz internal clock
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
init_fosc();
while(1);
}
What is the purpose of the PLL? It multiplies the 8MHz clock by 4 to reach 32MHz. Note that this only works with an 8MHz base frequency.
Setting the clock to 32MHz using the internal oscillator:
Development environment: MPLAB X IDE
Chip model: PICLF1823
#include <xc.h>
__CONFIG(FOSC_INTOSC&WDTE_OFF&PWRTE_ON&MCLRE_OFF&CP_ON&CPD_OFF&BOREN_ON&
CLKOUTEN_OFF&IESO_ON&FCMEN_ON); // Previous line continues here
__CONFIG(PLLEN_ON&LVP_OFF); // Enable PLL and set FOSC<2:0> to INTOSC
void init_fosc(void)
{
OSCCON = 0xF0; // Set 8MHz internal clock and enable 4X PLL
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
init_fosc();
while(1);
}
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com