**What is a Fieldbus?**
A fieldbus is a digital, two-way communication network used at the production site to connect intelligent field devices with automated measurement and control systems. It is located at the lowest level of the control hierarchy and serves as a bridge between the physical devices and higher-level systems.
Fieldbus is typically a low-bandwidth network designed for industrial environments, enabling communication between devices and the upper-level networks such as the internet or intranet. It forms a comprehensive communication platform that supports data exchange across different levels of an enterprise.
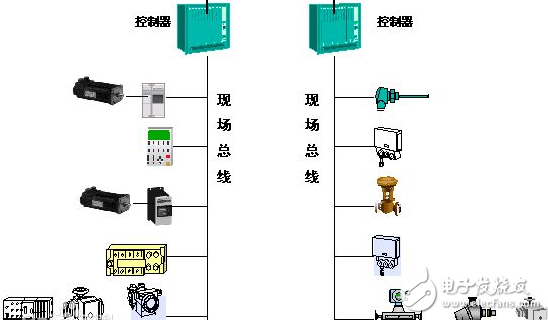
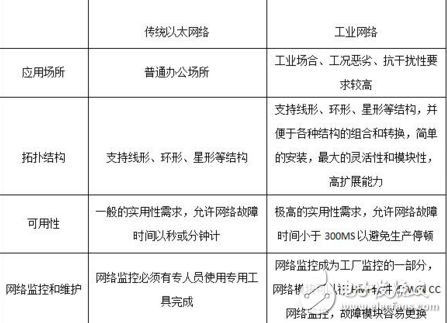
The image below illustrates the relationship between Industrial Ethernet and Fieldbus:
Interactive whiteboard,COB LED display,touch screen display,LCD whitboard,meeting tablet
Shanghai Really Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.really-led.com